Quantum News
Signal adds quantum-resistant encryption to its E2EE messaging protocol

25 Sep 2023: Signal has announced that it upgraded its end-to-end communication protocol to use quantum-resistant encryption keys to protect users from future attacks.
Signal explains that its “X3DH” (Extended Triple Diffie-Hellman) key agreement protocol has been upgraded to “PQXDH” (Post-Quantum Extended Diffie-Hellman), which incorporates quantum-resistant secret key generation mechanisms for Signal’s end-to-end encryption (E2EE) specification.
Intel Plans a Quantum Computing Approach to Leapfrog Rivals

21 Sep 2023: Intel is developing a successor to its Tunnel Falls quantum processor, aiming to leverage its expertise in silicon-based technology to improve qubit quality and scalability, potentially advancing applications in AI, materials science, and cryptography.
Physicists Create New Magnetic Material to Unleash Quantum Computing

18 Sep 2023: Researchers from the University of Texas, El Paso have developed a highly magnetic quantum computing material that retains its magnetism at room temperature. The material, which does not contain high-demand rare earth minerals, exhibits superparamagnetic behavior, making it a potential option for creating qubits, the basic unit of quantum information. By synthesizing the material in a sequential process, the researchers were able to produce a material 100 times more magnetic than pure iron.
When a Quantum Computer Is Able to Break Our Encryption, It Won't Be a Secret

13 Sep 2023: There is already more than enough reason to upgrade our communications systems to resist attacks from quantum computers as soon as possible. Even if completely unexpected attacks from a black-swan quantum computer are unlikely, attacks from known or suspected quantum computers would already be plenty bad enough.
Laser Precision Qubit Control: Leap in Reliable Quantum Information Processing

11 Sep 2023: Researchers have pioneered a groundbreaking technique utilizing laser light to control individual qubits made of barium more robustly than any other method currently known. Reliably controlling qubits is a critical step towards actualizing functional quantum computers of the future.
Chinese breakthrough a step towards scalable quantum computation: paper
10 Sep 2023: Chinese scientists have made a significant breakthrough in the development of practical processors for quantum computers. Previous studies were only able to entangle two atoms at a time, but the team was able to entangle eight and 10 ultracold atoms in two-dimensional blocks and one-dimensional chains respectively.
Checkmate! Quantum Computing Breakthrough Via Scalable Quantum Dot Chessboard

04 Sep 2023: Researchers at QuTech, a collaboration between the Delft University of Technology and TNO, have developed a new method for addressing quantum dots that could enable the operation of larger gate-defined quantum dot systems. The method uses a chessboard-like approach, where quantum dots are addressed using a combination of horizontal and vertical lines, similar to how chess pieces are addressed with letters and numbers. This approach reduces the number of control lines needed to address multiple qubits, potentially enabling the scaling up of quantum systems.
Quantum Machines Introduces OPX1000: The Quantum Control Solution for Large-Scale Quantum Computing

29 Aug 2023: Quantum Machines has launched its new advanced quantum control solution, OPX1000, which offers industry-leading performance metrics including feedback capabilities, runtime, analog performance, and channel density. The modular quantum controller is designed to scale control of quantum computers to 1000 qubits and beyond. The solution is currently being deployed with select customers and will be generally available later this year. OPX1000 is programmed using Quantum Machines’ intuitive pulse-level language, QUA, or at the gate level using the OpenQASM3 to QUA compiler extension.
IBM makes major leap in quantum computing error-detection
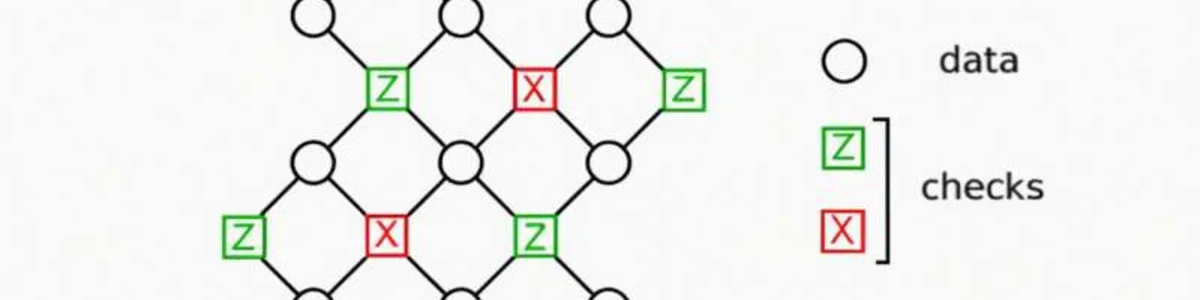
29 Aug 2023: IBM researchers have developed a system that improves error-detection in quantum computing, a major obstacle to its advancement. Quantum computers are highly sensitive to noise and prone to errors in their qubits. Unlike standard computer bits, qubits cannot be cloned without introducing errors. The researchers have developed an improved code and redesigned qubit placement that reduces the number of physical qubits needed for error-correction by one-tenth. While the approach currently only works on quantum memory and not computational power, it is seen as a step towards fault-tolerant quantum computing.
Post-Quantum Cryptography: CISA, NIST, and NSA Recommend How to Prepare Now

21 Aug 2023: The National Security Agency (NSA), Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) warned that cyber actors could target our nation’s most sensitive information now and leverage future quantum computing technology to break traditional non-quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms. This could be particularly devastating to sensitive information with long-term secrecy requirements.
“The transition to a secured quantum computing era is a long-term intensive community effort that will require extensive collaboration between government and industry.
Contact Us
Join our mailing list, contact the team or join our vibrant and friendly community of users, developers and enthusiasts on Discord or one of our other social channels

