New photonics approach enhances quantum computation efficiency
Nature Photonics Hebrew University of Jerusalem
9th October 2024
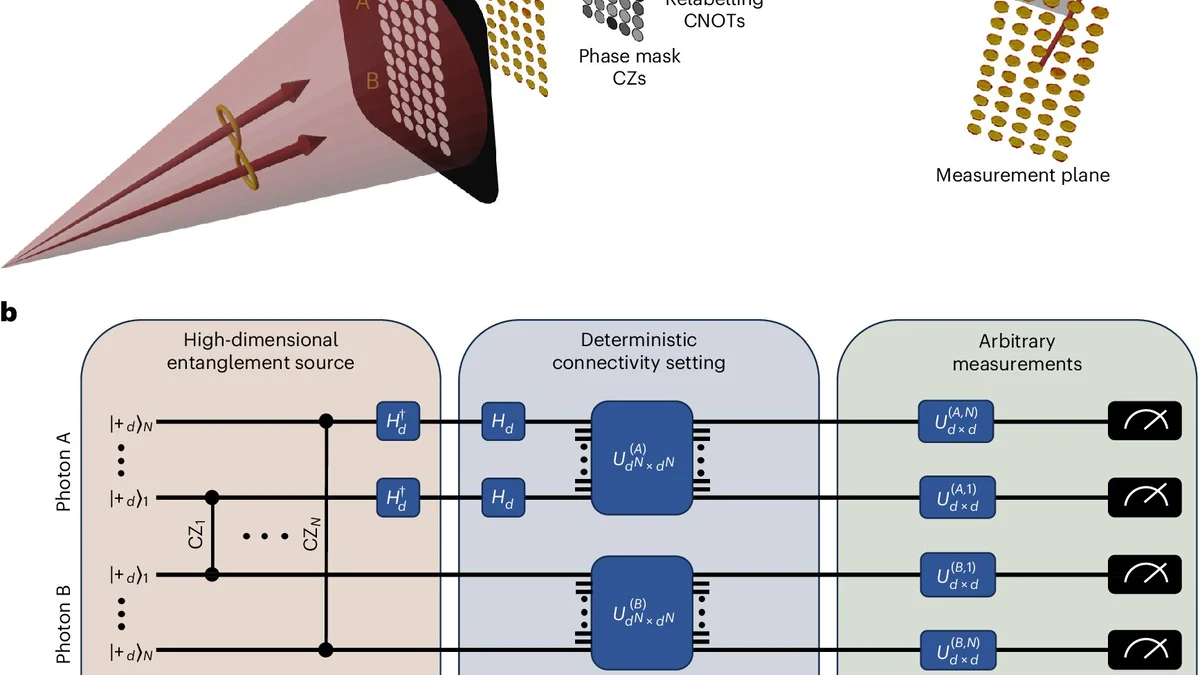
A recent study published in Nature Photonics by Prof. Yaron Bromberg and Dr. Ohad Lib from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem presents a significant advancement in quantum computing through photonic-measurement-based methods. Their research addresses the challenge of generating large cluster states, which are essential for quantum computations but difficult to produce due to exponentially decreasing detection probabilities as photon numbers increase. By using high-dimensional spatial encoding, they successfully encoded multiple qubits within each photon, creating cluster states with over nine qubits at a frequency of 100 Hz. This innovative approach not only enhances scalability but also reduces computation time by allowing instantaneous feedforward between qubits encoded within the same photon.
The implications of this breakthrough are substantial, as it opens new avenues for more resource-efficient and faster quantum computations, potentially leading to fault-tolerant quantum computers capable of tackling complex problems. Prof. Bromberg highlighted that their results demonstrate how high-dimensional encoding can overcome previous scalability barriers and offer a practical approach to quantum computing. Dr. Lib emphasized that their work addresses both scalability and computation duration challenges, paving the way for advancements in measurement-based quantum computation. This study marks an important milestone in harnessing the full potential of quantum computing using photonics.
9th October 2024
